Male sexual dysfunction causes are a complex and multi-faceted issue that affects many men worldwide. Erectile dysfunction, premature ejaculation, and low libido are common forms of male sexual dysfunction, and the causes can range from physical to psychological factors.
Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a group of conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels and there can be various underlying causes. It is one of the main diseases leading to deaths worldwide.
[source: exaly.com/journal/140545/american-journal-of-cardiovascular-disase/]
Prevanlence Of Cardiovascular Disaese in The US & The World
Here are some key statistics on the prevalence of CVD in the US and the world:
- In the United States, CVD is the leading cause of death for both men and women, accounting for about 1 in every 4 deaths. In 2020, it was estimated that approximately 18.6 million adults in the US had been diagnosed with CVD.
- Globally, CVD is also a leading cause of death, accounting for over 17 million deaths per year. It is estimated that by 2030, over 23 million people will die from CVD each year.
The causes of CVD are complex and multifactorial, but some of the key risk factors include:
- High blood pressure: High blood pressure (hypertension) is a major risk factor for CVD, as it can damage the arteries and make the heart work harder.
- High cholesterol: High levels of cholesterol in the blood can lead to the formation of plaque in the arteries, which can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Smoking: Smoking can damage the blood vessels and increase the risk of CVD.
- Diabetes: Diabetes can increase the risk of CVD, as high blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels and lead to atherosclerosis (narrowing of the arteries).
- Obesity: Obesity is a major risk factor for CVD, as it can increase the risk of high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes.
- Family history: A family history of CVD can increase the risk of developing the condition.
- Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can increase the risk of CVD, as it can lead to obesity, high blood pressure, and other risk factors.
- Stress: Chronic stress can increase the risk of CVD, as it can lead to high blood pressure, inflammation, and other risk factors.
By addressing these risk factors through lifestyle changes and medical treatments, it may be possible to reduce the incidence of CVD and improve cardiovascular health.
Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. It is a major public health problem worldwide, with significant implications for morbidity, mortality, and health care costs. Key statistics on the prevalence of diabetes mellitus in the US and the world are as follows:
- In the United States, diabetes affects approximately 34 million people, or 10.5% of the population. Another 88 million people have prediabetes, a condition in which blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes.
- Globally, an estimated 463 million people have diabetes, and this number is expected to increase to 700 million by 2045.
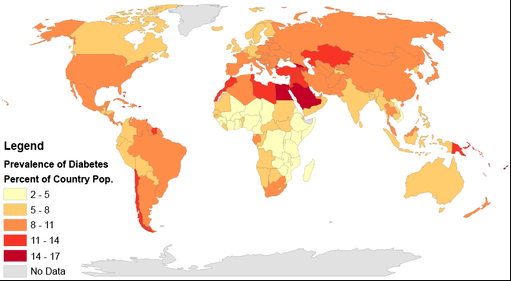
[source:Walter Scott Wilkens University of Illinois – Urbana Champaign Department of Geography and GIScience, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons]
Diabetes Mellitus Risk Factors
The causes of diabetes mellitus are complex and multifactorial, but some of the main risk factors include:
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes, as it can lead to insulin resistance, a condition in which the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin.
- Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of physical activity is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes, as it can contribute to obesity and insulin resistance.
- Family history: A family history of diabetes is a risk factor for developing the condition.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, including African Americans, Hispanics, Native Americans, and Asian Americans, are at higher risk for diabetes.
- Age: The risk of developing diabetes increases with age, especially after age 45.
- Gestational diabetes: Women who develop gestational diabetes during pregnancy are at higher risk for developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
- Other medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and sleep apnea, are associated with an increased risk of diabetes.
There are several types of diabetes mellitus, including type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin.
Type 2 diabetes is the most common type, and it is characterized by insulin resistance and/or insufficient insulin production.
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy and usually goes away after delivery.
Prevention and management of diabetes mellitus typically involve lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet, increasing physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Medications, including insulin and oral medications, may also be prescribed to manage blood sugar levels.
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and other health parameters, such as blood pressure and cholesterol, is also important to prevent and manage diabetes and its complications.
High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a common health condition characterized by elevated blood pressure in the arteries.
It is a major public health concern worldwide, with significant implications for cardiovascular health, morbidity, and mortality.
Some key statistics on the prevalence of high blood pressure in the US and the world are:
- In the United States, approximately 45% of adults have high blood pressure, which translates to over 100 million people. However, only about half of these individuals have their blood pressure adequately controlled.
- Globally, an estimated 1.13 billion people have high blood pressure, making it one of the most common health conditions worldwide.
The causes of high blood pressure are also complex and multifactorial.
Some of the key risk factors include:
- Unhealthy diet: Consuming a diet high in salt, saturated and trans fats, and added sugars can increase the risk of developing high blood pressure.
- Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of physical activity is a risk factor for high blood pressure, as it can contribute to obesity and insulin resistance.
- Family history: A family history of high blood pressure is a risk factor for developing the condition.
- Age: The risk of developing high blood pressure increases with age, especially after age 60.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, including African Americans, Hispanics, and Native Americans, are at higher risk for high blood pressure.
- Smoking: Tobacco use is a risk factor for high blood pressure and cardiovascular disease.
- Alcohol consumption: Consuming excessive amounts of alcohol can increase blood pressure.
High blood pressure is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease, including heart attack and stroke. Prevention and management of high blood pressure typically involve lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet, increasing physical activity, limiting alcohol and tobacco use, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Medications, such as diuretics, beta blockers, and ACE inhibitors, may also be prescribed to manage blood pressure.
Regular monitoring of blood pressure and other health parameters is important to prevent and manage high blood pressure and its complications.
Obesity
Obesity is a serious health condition characterized by excess body fat that can lead to a range of health problems, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
Here are some facts on the prevalence, causes, treatment options, and surgery for obesity:
Obesity Prevalence
- In the United States, more than one-third of adults (nearly 40%) are obese, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
- Globally, the prevalence of obesity has nearly tripled since 1975, with an estimated 650 million adults and 124 million children affected in 2016.
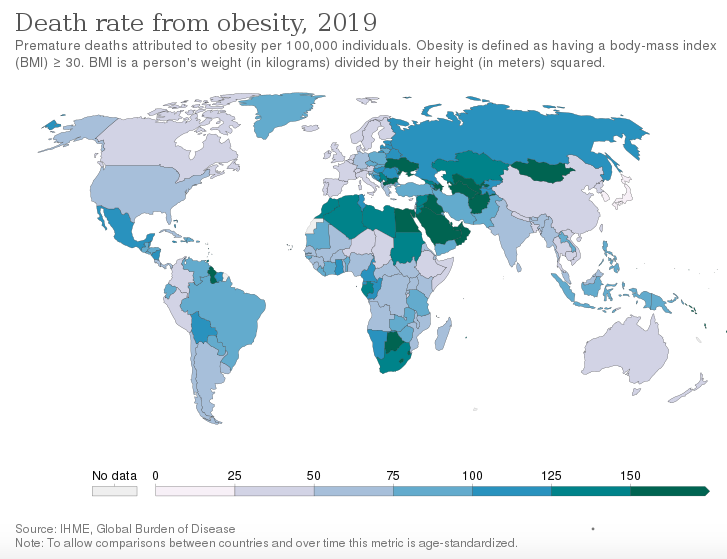
[source:https://ourworldindata.org/death-rate-from-obesity]
Obesity Causes
- Obesity is a complex condition with multiple causes, including genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
- Poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, and lack of physical activity are common risk factors for obesity.
- Genetic factors can also play a role in obesity, as certain genes may affect appetite, metabolism, and fat storage.
Obesity Treatment Options
- Lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet, increasing physical activity, and achieving and maintaining a healthy weight, are the first line of treatment for obesity.
- Medications, such as appetite suppressants or drugs that block fat absorption, may also be prescribed in certain cases.
- Bariatric surgery, which includes procedures such as gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and adjustable gastric banding, is a treatment option for severe obesity when other treatments have not been successful.
- These procedures can lead to significant weight loss and improvement in obesity-related health conditions, but they also carry risks and require long-term follow-up care.
Prostate Disease & Cancer
Prostate problems are common among men, especially as they age. Here are some key facts on the prevalence, causes, and treatment options of prostate problems:
Prevalence:
- Prostate problems are among the most common health problems for men, affecting about 50% of men over age 50 and up to 90% of men over age 80.
- Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer among men worldwide, with over 1.4 million new cases diagnosed each year.
Prostate Disease Causes
- The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system that can be affected by a variety of conditions, including inflammation, infection, enlargement, and cancer.
- Risk factors for prostate problems include age, family history, and certain lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise.
- Prostate cancer has also been linked to genetic mutations and exposure to certain chemicals and toxins.
[source: by Exaly]
Prostate Disease Treatment Options
- Treatment for prostate problems depends on the specific condition and its severity.
- For benign prostate conditions, such as an enlarged prostate or prostatitis, treatment options may include medication, lifestyle changes, and minimally invasive procedures.
- Treatment for prostate cancer may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and other targeted therapies.
- In some cases, “watchful waiting” or active surveillance may be recommended, particularly for slow-growing or early-stage prostate cancer.
- Penile traction or vacuum devices have been shown to be effective in men with ED caused by radical prostatectomy (prostate cancer surgery)
Kidney Disease & Injury
Kidney disease and kidney injury are two different conditions that can affect the function of the kidneys, which are vital organs responsible for filtering waste and excess fluid from the blood. Here are some key facts on the prevalence, causes, and treatment options for kidney disease and kidney injury:
Prevalence
- Kidney disease is a common health problem, affecting around 10% of the global population, and is a leading cause of death worldwide.
- In the United States, kidney disease affects an estimated 37 million people, or about 15% of the adult population.
- Acute kidney injury (AKI), which is a sudden loss of kidney function, is a common complication in hospitalized patients, affecting up to 20% of all hospitalized patients and up to 50% of those in intensive care units.
Causes
- Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is usually caused by underlying conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease, as well as lifestyle factors like obesity and smoking.
- Acute kidney injury can be caused by a variety of factors, including dehydration, medication toxicity, infections, and kidney stones.
Treatment options
- Treatment for kidney disease and injury depends on the specific condition and its severity.
- For chronic kidney disease, treatment may include medication, lifestyle changes, and in some cases, dialysis or kidney transplant.
- Acute kidney injury may require hospitalization and supportive care, including intravenous fluids and medications to manage symptoms.
- In both cases, early detection and management of underlying conditions, as well as regular monitoring of kidney function, are important for preventing further damage and improving outcomes.
In summary, kidney disease and kidney injury are common health problems that can have serious consequences if left untreated.
Causes vary depending on the specific condition, but often involve underlying health conditions and lifestyle factors.
Treatment options depend on the severity and may include medication, lifestyle changes, and in some cases, more intensive interventions like dialysis or transplant.
Regular monitoring and early intervention are key to managing kidney disease and improving outcomes.
MS & The Link To Sexual Dysfunction
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system, causing damage to the myelin sheath that surrounds and protects nerve fibers.
This can lead to a range of symptoms, including muscle weakness, difficulty with coordination and balance, and problems with vision and sensation.
Prevalence
- According to the National MS Society, there are approximately 1 million people living with MS in the United States.
- MS is more common in certain regions, with higher prevalence rates seen in North America, Europe, and Australia.
- Globally, MS affects an estimated 2.5 million people.
Causes
- The exact cause of MS is not known, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
- Some of the factors that may contribute to the development of MS include viral infections, vitamin D deficiency, smoking, and exposure to certain toxins.
Treatment options
- There is currently no cure for MS, but there are a variety of treatment options available to help manage symptoms and slow the progression of the disease.
- Medications such as corticosteroids and disease-modifying therapies can help reduce inflammation and prevent further damage to the nervous system.
- Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy can also be beneficial for managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
Link with sexual dysfunction
- MS can affect sexual function in both men and women, with symptoms including reduced libido, erectile dysfunction, difficulty with arousal and orgasm, and decreased vaginal lubrication.
- The specific symptoms can vary depending on the individual and the location and extent of nerve damage.
- Treatment options for sexual dysfunction related to MS may include medications such as sildenafil or tadalafil, as well as counseling and therapy to address emotional and psychological factors that may be contributing to the problem.
ALS & Its Relation To Sexual Dysfunction
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord.
It leads to muscle weakness, difficulty with speaking, swallowing, and breathing, and eventually paralysis.
Prevalence
- In the United States, approximately 5,000 people are diagnosed with ALS each year, and there are currently around 20,000 people living with the disease.
- ALS is more common in people between the ages of 40 and 70, and is slightly more common in men than in women.
- Globally, it is estimated that approximately 450,000 people have ALS.
Causes
- The exact cause of ALS is not known, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
- One study showed a link between severe magnesium deficiency and ALS
- Some of the factors that may contribute to the development of ALS include exposure to toxins, viral infections, and physical trauma.
Treatment options
- There is currently no cure for ALS, and treatment is focused on managing symptoms and slowing the progression of the disease.
- Medications such as riluzole and edaravone can help slow the progression of the disease and improve quality of life for some patients.
- Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy can also be beneficial in managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
Link with sexual dysfunction
- ALS can affect sexual function in both men and women, with symptoms including reduced libido, erectile dysfunction, difficulty with arousal and orgasm.
- The specific symptoms can vary depending on the individual and the location and extent of nerve damage.
- Treatment options for sexual dysfunction related to ALS may include medications such as sildenafil or tadalafil, as well as counseling and therapy to address emotional and psychological factors that may be contributing to the problem.
In summary, ALS is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord, leading to muscle weakness and eventual paralysis.
There is currently no cure for ALS, and treatment is focused on managing symptoms and slowing the progression of the disease.
Peyronie’s & Hourglas Peyronie’s Disease
Peyronie’s disease is a condition that affects the penis, causing it to become curved or bent during an erection, and is often associated with pain and difficulty with sexual intercourse.
Hourglass Peyronie’s disease is a specific type of Peyronie’s disease in which the penis has an hourglass-like shape, with a narrowed or constricted area in the middle.
Prevalence
- The exact prevalence of Peyronie’s disease and Hourglass Peyronie’s disease is unknown, as many men may not seek treatment or may not realize they have the condition.
- Estimates suggest that Peyronie’s disease affects around 1% of men worldwide, with the prevalence increasing with age.
Causes
- The exact cause of Peyronie’s disease is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve the development of scar tissue (plaque) within the penis, which can cause curvature or narrowing.
- Risk factors for Peyronie’s disease include genetics, age, trauma or injury to the penis, and certain medical conditions such as diabetes.
Treatment options
- Treatment for Peyronie’s disease and Hourglass Peyronie’s disease depends on the severity of symptoms and may include medication, injections, shockwave therapy, or surgery.
- In some cases, treatment may not be necessary if symptoms are mild and do not interfere with sexual function.
- In cases where Peyronie’s disease is associated with erectile dysfunction (ED), penile traction devices are an effective means of reducing curvature and treating ED
Link with ED
- Peyronie’s disease and Hourglass Peyronie’s disease can be associated with ED, as the curvature or narrowing of the penis can affect blood flow and cause difficulty with erections.
- Treatment for ED can be applied in conjunction with treatment for Peyronie’s disease, depending on the severity of symptoms and underlying causes.
In summary, Peyronie’s disease and Hourglass Peyronie’s disease are conditions that can affect the penis, causing curvature or narrowing and often associated with pain and difficulty with sexual function.
The exact causes are not fully understood, but treatment options are available depending on the severity of symptoms.
In recent years, penile traction devices have gained attention for the correction of penile curvature and the concomitant treatment of erectile dysfunction in men with Peyronie’s disease. The famous Mayo Clinic announces that these devices offer safer and effective alternative to penile surgery. For further information, see here.
What Medicine Causes Erectile Dysfunction
Common Types of Medications That May Cause ED
- Blood Pressure Medications
- Hormonal Therapies
- Antidepressants
- Acid Reflux Medications
- Anti-Anxiety Medications
Studies Linking Medications and Erectile Dysfunction
- Blood Pressure Medications: Some blood pressure medications can cause ED as a side effect. These medications include diuretics, beta-blockers, and ACE inhibitors.
- In a study published in the Journal of Hypertension, researchers found that men taking beta-blockers were more likely to experience ED than those not taking them.
- Antidepressants: Certain antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), can also cause ED.
- A study published in the Journal of Sexual Medicine found that men taking SSRIs were more likely to experience ED than those not taking them.
- Anti-Anxiety Medications: Benzodiazepines, a type of anti-anxiety medication, can also cause ED.
- In a study published in the Journal of Sexual Medicine, researchers found that men taking benzodiazepines were more likely to experience ED than those not taking them.
- Acid Reflux Medications: Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), a type of medication used to treat acid reflux, have been linked to ED.
- A study published in JAMA Internal Medicine found that men taking PPIs were more likely to experience ED than those not taking them. Here you can find almost evrything on heartburn, acid reflux disease and effective treatment.
- Statins: Statins are medications used to lower cholesterol levels, but they have been linked to ED as a side effect.
- A study published in the Journal of Sexual Medicine found that men taking statins were more likely to experience ED than those not taking them.
Conclusion:
While medication can be essential for treating various health conditions, it’s important to understand the potential side effects, including ED.
It’s important that not everyone who takes these medications experience ED, and there may be other factors contributing to sexual dysfunction.

